Cats, like all animals, are susceptible to bacterial infections. Some infections can cause mild symptoms, while others may lead to severe illness if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the common bacterial diseases of cats and discuss ways to keep your feline companions safe and healthy. Understanding these common bacterial diseases of cats is essential for early detection and proper treatment. By learning about the common bacterial diseases of cats, you can ensure that your furry friends remain healthy and happy.
1. Bordetellosis
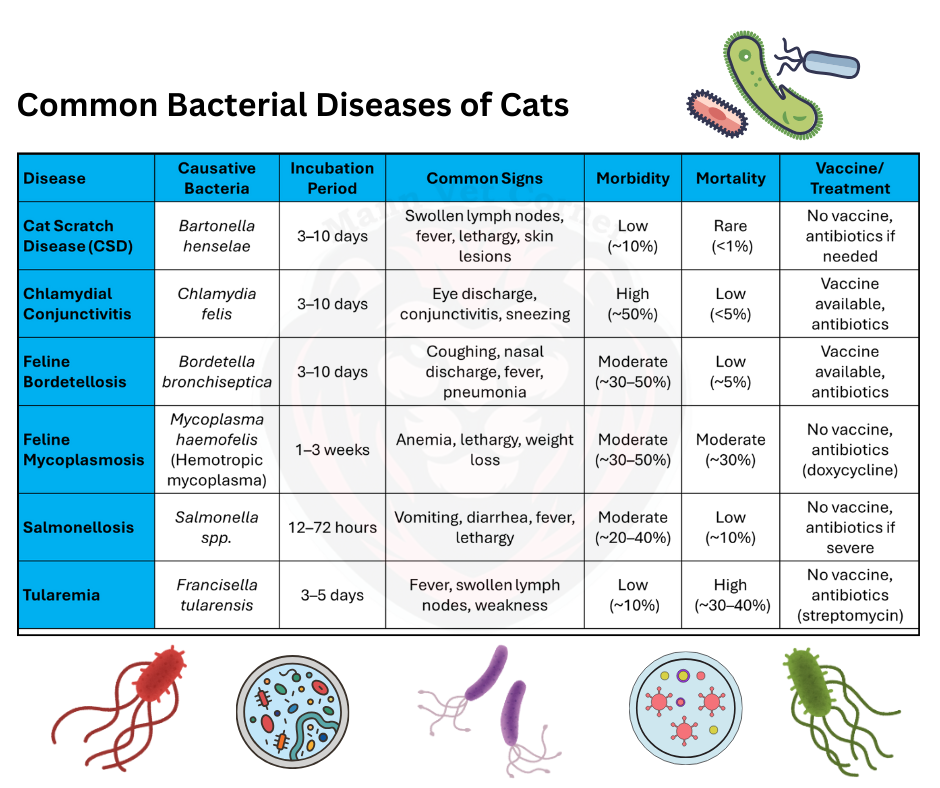
Bordetellosis, a disease affecting the respiratory system, is caused by the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica. This highly contagious bacterium can spread through direct contact, airborne droplets, and contaminated surfaces, often leading to symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, and nasal discharge in affected cats.
Symptoms:
- Sneezing and nasal discharge
- Coughing
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
Prevention & Treatment:
Vaccination can help prevent infection. Veterinarians commonly prescribe antibiotics to treat bordetellosis. They also recommend supportive care measures, such as ensuring the cat stays adequately hydrated and receives proper nutrition. These combined efforts help manage the infection and promote a swift recovery.
2. Feline Chlamydiosis
The bacterium Chlamydia felis causes feline chlamydiosis, a disease that primarily affects the eyes and respiratory system. This bacterial infection often presents symptoms such as conjunctivitis, sneezing, and nasal discharge.
Symptoms:
- Conjunctivitis (eye inflammation)
- Watery or pus-like eye discharge
- Sneezing
- Lethargy
Prevention & Treatment:
Vaccination is available for prevention. Antibiotics such as doxycycline are commonly used for treatment.
3. Salmonellosis
Salmonella bacteria typically cause salmonellosis, which people usually contract through contaminated food, water, or exposure to infected prey.
Symptoms:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Dehydration
Prevention & Treatment:
Avoid feeding raw diets and ensure proper food hygiene. Treatment includes antibiotics and fluid therapy to prevent dehydration.
4. Pasteurellosis
Cats often transmit Pasteurella multocida, a common bacterium in their mouths, through bites and scratches, leading to symptoms such as swelling, abscess formation, fever, and pain at the wound site.
Symptoms:
- Swelling and abscess formation
- Pain at the wound site
- Fever
- Lethargy
Prevention & Treatment:
Prompt wound cleaning and antibiotic treatment are essential. Vaccinations may help reduce risk.
5. Mycoplasmosis
Mycoplasma species cause feline mycoplasmosis, affecting red blood cells and leading to anemia.
Symptoms:
- Pale gums
- Weakness and lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Rapid breathing
Prevention & Treatment:
Regular veterinary checkups and parasite control can reduce infection risk. Antibiotics such as doxycycline are commonly prescribed.
6. Tularemia
Tularemia, or “rabbit fever,” is caused by Francisella tularensis. Cats typically contract it by hunting infected prey.
Symptoms:
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Ulcers on the skin
- Jaundice
Prevention & Treatment:
Keep cats indoors to prevent exposure. Antibiotics like streptomycin or doxycycline are effective treatments.
Conclusion
Bacterial infections in cats can vary from mild to severe, but you can help keep your feline friend safe with proper preventive measures. These include vaccinations, maintaining hygiene, and ensuring regular veterinary care. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a quick recovery.
